Today's Topics
- Recap on last week
- Control flow
- Loops
- Creating your own functions
Recap: Plotting
Matplotlib's plot function takes two arrays and produces a 2D plot:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
plt.plot(x, y)
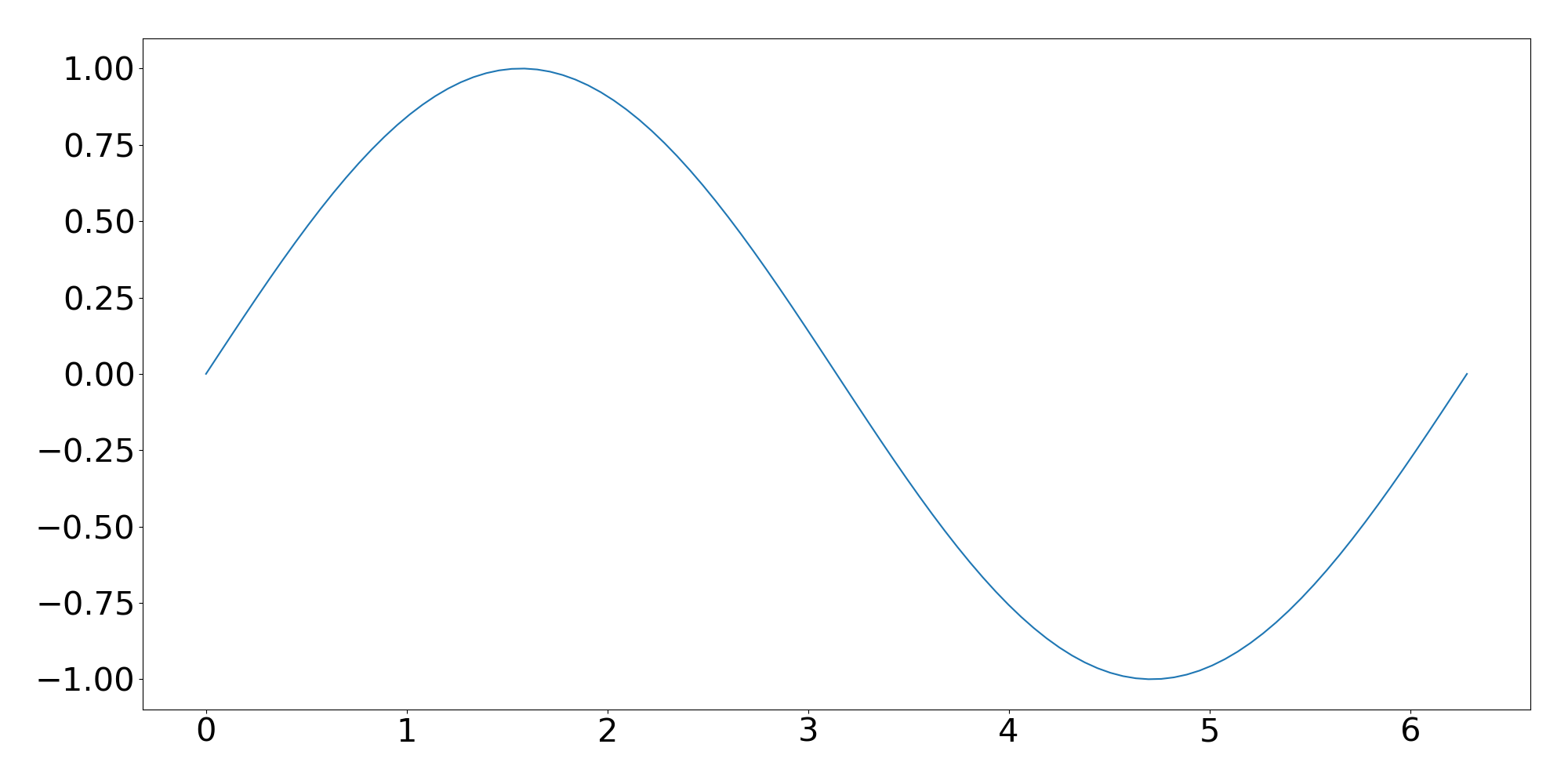
Download the full source code for this plot.
Methods such as xlabel, ylabel and title can be used to make the plot look nice:
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('y = sin(x)')
plt.xlim(0, 2*np.pi)
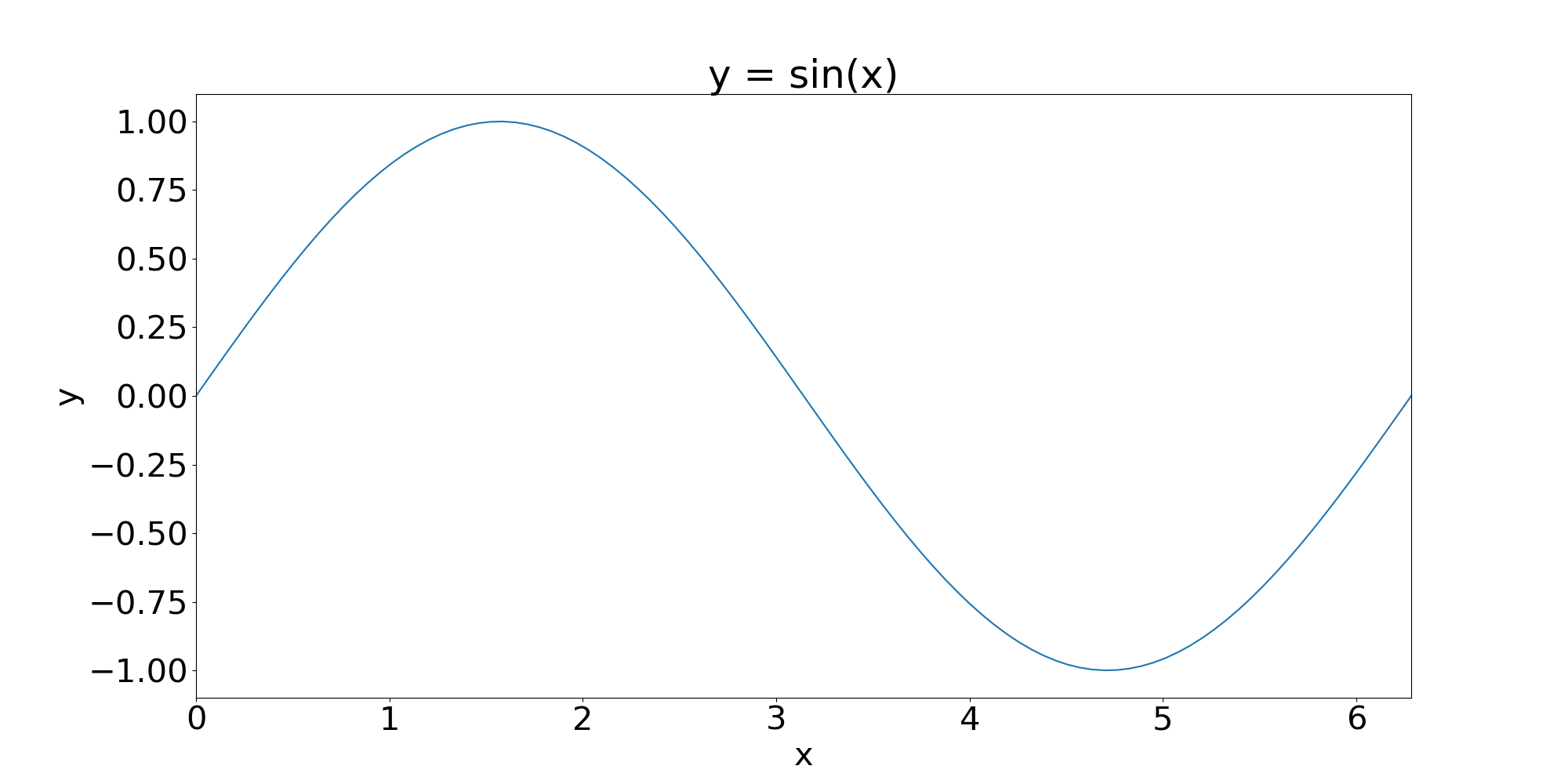
Download the full source code for this plot
Control Flow
Control flow statements are used to determine if and when commands in your code are carried out. Control flow is part of the staple diet for almost all programming languages.
We're going to look at three types of construct which control the flow of a piece of computer code:
- If statements
- For loops
- While loops
Control flow concepts
Let's consider these in turn conceptually, before we look at the Python syntax.
If statements
An if statement is used to specify that a command(s) that is only executed if a condition is satisfied.
Note: in case it isn't clear, these are not Python commands! This is a made-up language called pseudocode.
If something is true
Do something
e.g. Choosing what you do on the metro:
If it is Monday
Listen to music
This can be extended to if...else statements:
If something is true
Do something
else
Do something else
e.g. Choosing what you do on the metro:
If remembered to bring headphones
Listen to music
else
Read the newspaper
For loops
A for loop repeats a specified command or list of commands several times in succession
For some list of things
Do something
e.g. reading a newspaper on the metro
For each page in the Metro newspaper
Read the page
The for loop can contain many commands. And often there is a counter: here it might be our page number
For x = each page in the Metro newspaper
Read page x
Check location on the metro map
Check phone for messages
While loops
A while loop is similar to a for loop, but in this case the loop is repeated only whilst a condition is satisified.
While something is true
Do something
E.g. reading a newspaper til you reach your destination:
While on the train
Read a newspaper page
Turn to the next page
Note that if you need a counter then you need to set it yourself
x = 0
While on the train
x = x + 1
Read page x
Similar ideas have been used in music for many centuries...


Control flow in Python
Now let's take a look at control flow in Python
If statements
x = 2
if x > 0:
print('it is true') # Print something if trueNote that it is required to indent the contents of the if statement!
For loops
for i in range(1,6):
print(i) # useful function to display iWhile loops
x = 0
while x < 5:
x = x + 1
print(x) # display x at this iterationApplications of control flow
Loops and if statements are essential blocks of computer code and we'll have a look at some examples of how to use them in the handout this week.
Here's an example of plotting multiple curves, adapting and example from last week.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Create the x axis
x = np.linspace(0, 6, 200)
# Create 3 plots in a loop
for i in range(1, 4):
plt.plot(x, np.sin(i*x))
# Add axis labels etc.
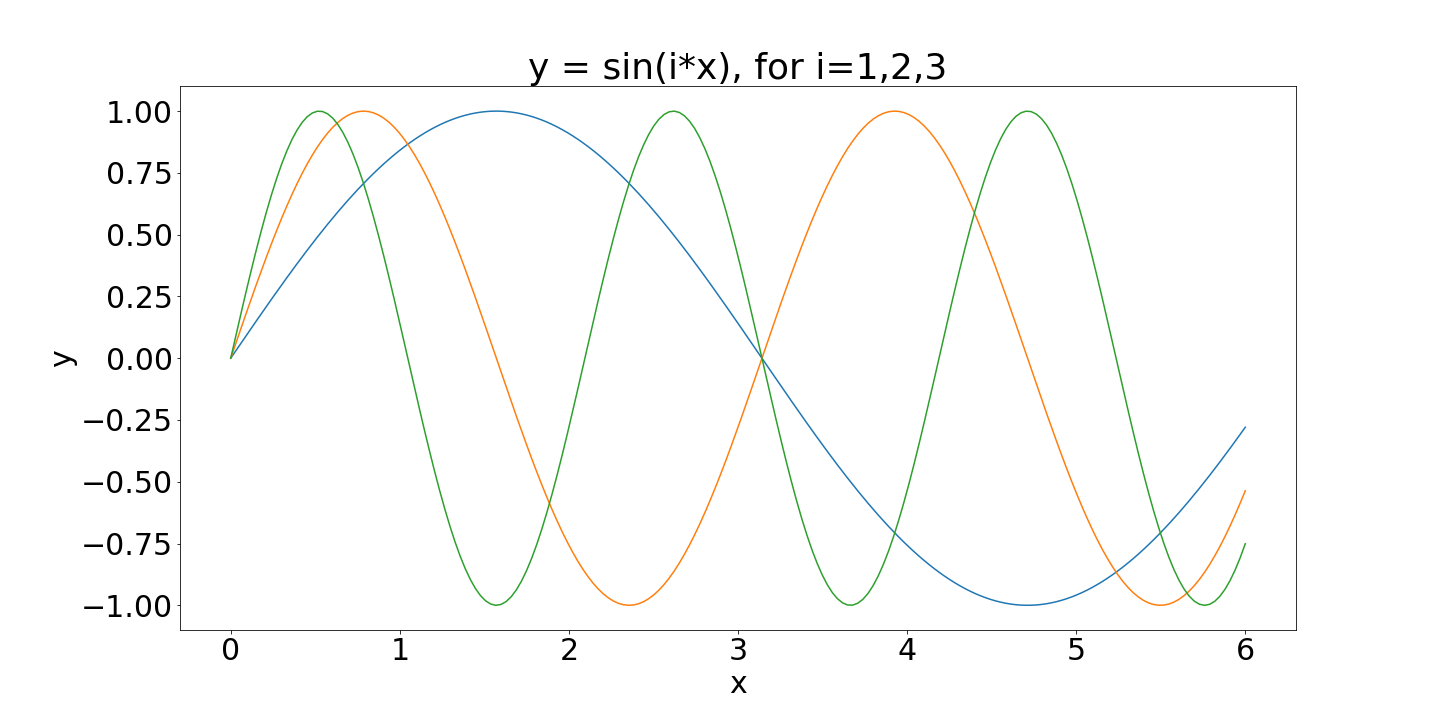
Download the full source code for this plot
Functions
-
So far we have made use of a variety of built-in functions. And today we are going to see how to create our own.
-
Splitting up computer code by writing user-defined functions is a very good idea, and Python has a couple of options for separating chunks of code out into a function.
The syntax for creating a function is as follows:
def my_func():
print("My function prints this")
Note a similar syntax and indenting as for control flow
The function begins with the keyword def and then the function name "my_func".
Input arguments are defined inside brackets - for this function there are none
Once defined, we can use the function by running:
my_func()
Let's add an argument:
def square_a_number(x):
return x**2
The argument x has been added. You provide a value for it when you "call" the function
The return statement controls what value (or values) your function outputs
x = square_a_number(3)
print(x)
9Handling errors
During your work in the practicals, you have probably encountered a bit of red text and errors that occur when you run commands Python has a problem with.
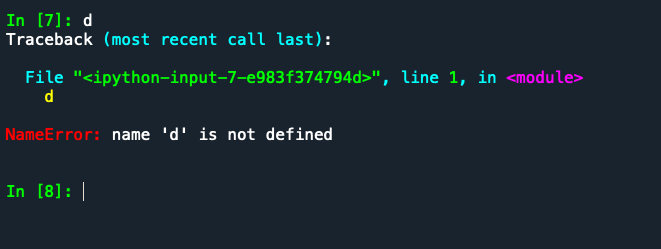
You can create your own error messages in your code too!
The raise function displays a message in red, and halts execution of the code.
raise(Exception('This is a custom error message!'))
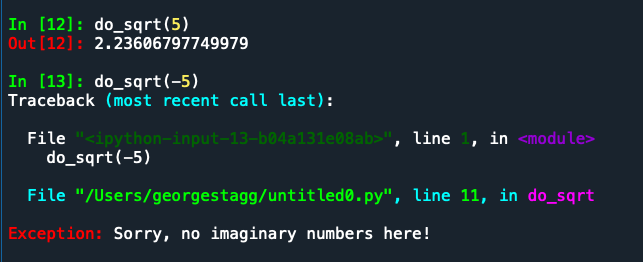
For example,
def do_sqrt(x):
if x < 0:
raise(Exception("Sorry, no imaginary numbers here!"))
else:
return x**0.5
Adding help
A comment contained within three quotes """ at the start of our custom function is used to display help. It is known as a docstring (documentation string)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def sin_plus_cos(x):
""" Takes in a value x and
returns cos(x)+sin(x) """
return np.cos(x)+np.sin(x)
Test your help with
help(sin_plus_cos)
Algorithmic thinking
algorithm
noun
a process or set of rules to be followed in calculations or other problem-solving operations, especially by a computer.
The following is a worked example...
Numerical Solutions to differential equations
Differential equations play a part in almost every model of physical processes: from the fundamental laws of physics, to population growth, chemical reactions and economic modelling.
We are (or at least you will be later on) interested in solving differential equations, for example
Why Python?
- This problem can be solved using pen and paper, but that is not always the case!
- We can use Python as a powerful visualisation tool
Euler's Method
Let's derive a method to solve this ODE on a computer, simply by applying some problem solving...
We want to know how evolves with .

Euler's Method Algorithm
For first order differential equations of the form
Euler's Method approximates the solution using
We can write our algorithm for this problem as:
as a function
def f(y):
return -y/2
and a for loop (I've chosen )
y = np.zeros(10)
y[0] = 5
for n in range(1, 10):
y[n] = y[n-1]+0.5*f(y[n-1])
print(y)
plt.plot(y)
Lecture 3 Summary
Creating our own functions and being able to control when commands are used using loops and if statements will bring us new powers to process data, plot and more. In the handout we'll apply some of these ideas to some more algorithms.